Recent research conducted by the University of Kaiserslautern-Landau (RTPU), on behalf of Qualcomm Europe Inc., highlights the potential of connected vehicle applications to significantly decrease CO2 emissions in the transportation industry.
The study focused on city optimization applications such as dynamic traffic signals, traffic junctions, and routing, which aim to reduce start-stops and traffic congestion, thus enhancing travel efficiency and time. The findings of the study demonstrate that the introduction of only 20% of connected vehicles on EU city roads can lead to a reduction of up to 18% in CO2 emissions.
In some EU27 countries, such as Germany, the potential emissions savings could even reach up to 24%. This significant progress in the reduction of transport-related emissions aligns with the EU Green Deal targets, in which the EU Commission strives to achieve a 90% reduction in such emissions by 2050.
The study utilized a novel simulation approach, extrapolating results from in-depth map-based traffic simulations in selected cities to all EU27 Member States cities. The research predicts that cities with populations ranging from fewer than 100,000 to greater than 500,000 can benefit from the advantages of connected vehicles, leading to reduced emissions and increased traffic efficiency. Furthermore, drivers can expect to save up to 15 hours of travel time annually during peak hours, resulting in higher productivity and comfort levels.
“The results of this study show how technology can help reduce emissions, making road transport more efficient and sustainable without compromising the safety of road users,” said Enrico Salvatori, Senior Vice President and President, Qualcomm Europe/MEA, Qualcomm Europe Inc.
“Utilizing our highly advanced Snapdragon® Digital Chassis™ automotive solutions spanning telematics and connectivity, the digital cockpit and driver assistance and vehicle automation, we are supporting automakers to design and deliver next-generation connected and autonomous vehicles. The RTPU study marks an important milestone towards the widespread adoption of connected mobility and greener, more efficient road transport for all.”
“This study impressively demonstrates the potential of connected mobility applications to reduce emissions in the transport sector. We have learned that already simple combinations of connected mobility applications and realistic penetration rates of connected vehicles allow significant reductions in emissions to be achieved, without having to compromise on driver comfort,” said Professor Dr. Hans D. Schotten, RTPU.
The study focused on city optimization applications such as dynamic traffic signals, traffic junctions, and routing, which aim to reduce start-stops and traffic congestion, thus enhancing travel efficiency and time. The findings of the study demonstrate that the introduction of only 20% of connected vehicles on EU city roads can lead to a reduction of up to 18% in CO2 emissions.
In some EU27 countries, such as Germany, the potential emissions savings could even reach up to 24%. This significant progress in the reduction of transport-related emissions aligns with the EU Green Deal targets, in which the EU Commission strives to achieve a 90% reduction in such emissions by 2050.
The study utilized a novel simulation approach, extrapolating results from in-depth map-based traffic simulations in selected cities to all EU27 Member States cities. The research predicts that cities with populations ranging from fewer than 100,000 to greater than 500,000 can benefit from the advantages of connected vehicles, leading to reduced emissions and increased traffic efficiency. Furthermore, drivers can expect to save up to 15 hours of travel time annually during peak hours, resulting in higher productivity and comfort levels.
“The results of this study show how technology can help reduce emissions, making road transport more efficient and sustainable without compromising the safety of road users,” said Enrico Salvatori, Senior Vice President and President, Qualcomm Europe/MEA, Qualcomm Europe Inc.
“Utilizing our highly advanced Snapdragon® Digital Chassis™ automotive solutions spanning telematics and connectivity, the digital cockpit and driver assistance and vehicle automation, we are supporting automakers to design and deliver next-generation connected and autonomous vehicles. The RTPU study marks an important milestone towards the widespread adoption of connected mobility and greener, more efficient road transport for all.”
“This study impressively demonstrates the potential of connected mobility applications to reduce emissions in the transport sector. We have learned that already simple combinations of connected mobility applications and realistic penetration rates of connected vehicles allow significant reductions in emissions to be achieved, without having to compromise on driver comfort,” said Professor Dr. Hans D. Schotten, RTPU.


 New Study Shows Connected Vehicles Can Reduce CO2 Emissions by Up to 18% in EU Cities
New Study Shows Connected Vehicles Can Reduce CO2 Emissions by Up to 18% in EU Cities



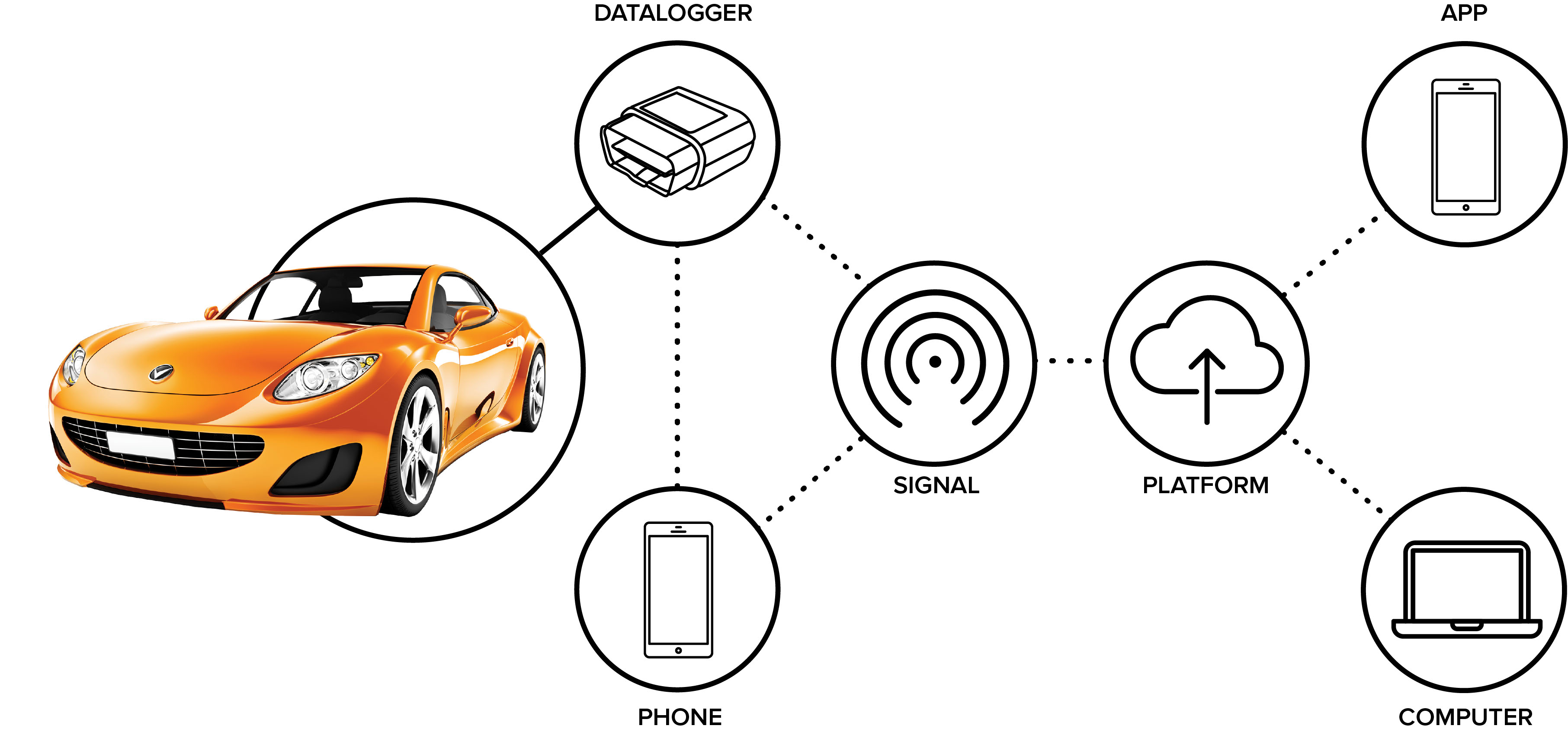
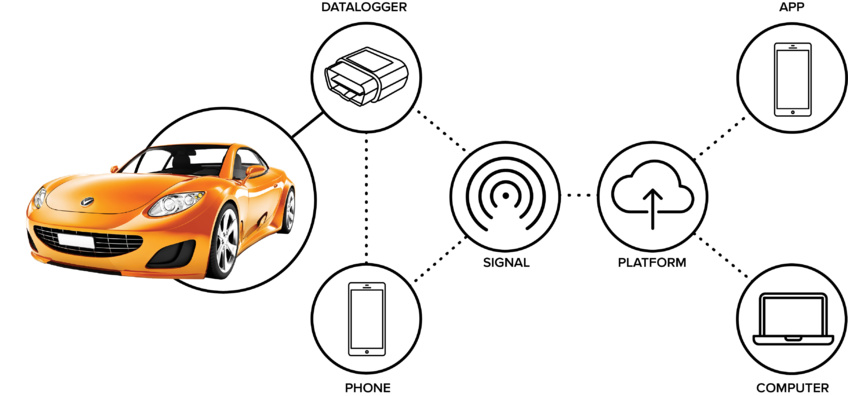
 Companies
Companies